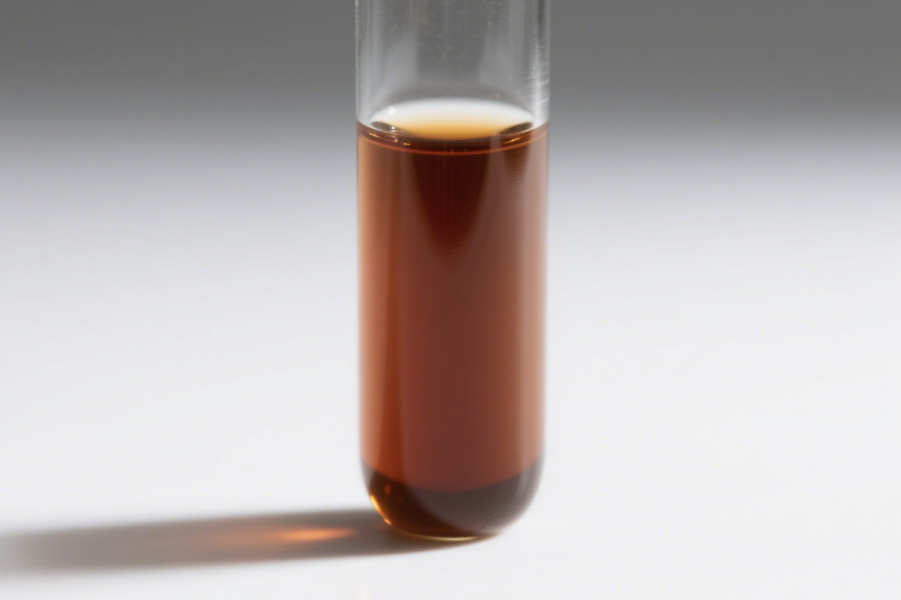
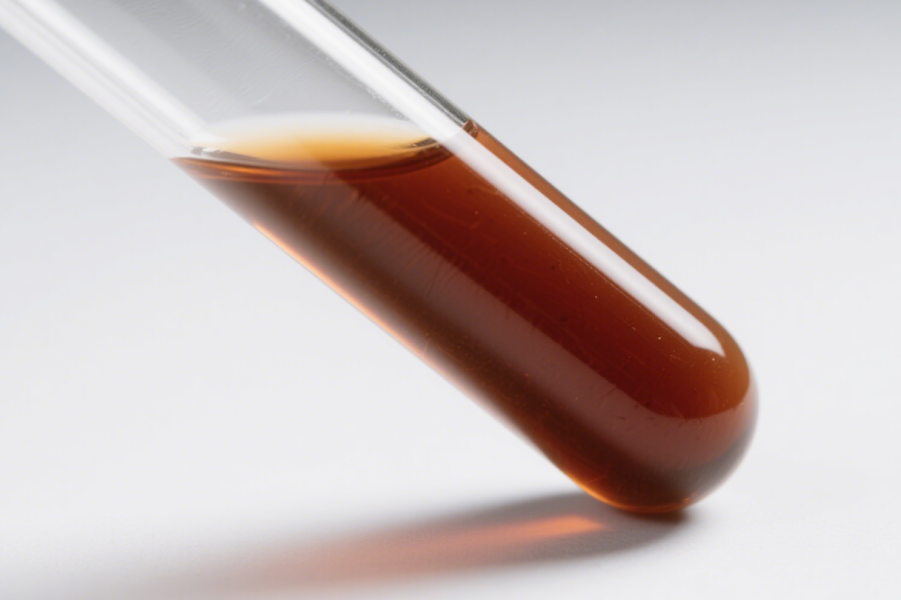
Palladium Nitrate Solution(CAS:10102-05-3) is an aqueous solution of palladium(II) nitrate (Pd(NO₃)₂), widely used in catalyst preparation, hydrogenation, electronic materials, and nanotechnology research. Its good solubility and reducibility make it a versatile palladium precursor in both laboratory and industrial settings.
Application 1: Catalyst Precursor for Cross-Coupling Reactions
Why It Matters
Cross-coupling reactions (Suzuki, Heck, Stille) are essential in pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and materials science. palladium nitrate solution serves as a reliable source for preparing both supported and homogeneous Pd catalysts.
Key Notes
Supports: activated carbon, SiO₂, Al₂O₃
Pd loading: 0.5–5 wt%
Reduction: H₂ or alcohol thermal reduction at 100–300 °C
Advantage: Controllable Pd dispersion for high catalytic activity and selectivity
Application 2: Supported Catalysts for Hydrogenation and Hydrogen Transfer
Why It Matters
Hydrogenation is a backbone process in petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals. palladium nitrate solution is widely applied to create hydrogenation catalysts.
Key Notes
Common supports: carbon, alumina
Pd loading: 1–5 wt%
Reaction conditions: 1–10 bar H₂, room temperature to 100 °C (lab scale)
Challenges: Pd poisoning by sulfur, halogens, oxygenates
Solution: Proper regeneration and doping to maintain selectivity
Application 3: Electronic Materials and Metallization
Why It Matters
With the growth of printed electronics and microelectronics, palladium nitrate solution is used in conductive inks, plating activation, and seed layers for electroless plating.
Key Notes
Method: Pd deposition on non-conductive substrates via reduction (formaldehyde, hypophosphite, mild heat)
Uses: contact repair, printed circuit traces, thin conductive films
Important: Adhesion, particle size control, and post-treatment (sintering/cure)
Environmental note: Pd recovery from waste streams reduces cost and environmental impact
Application 4: Hydrogen Sensors and Fuel Cell Electrode Modification
Why It Matters
Hydrogen detection and energy technologies rely on Pd’s unique hydrogen absorption properties.
Key Notes
Uses: Pd-modified electrodes, thin films, nanoparticle coatings
Preparation: impregnation-reduction, electrodeposition, sputtering
Challenges: hydrogen embrittlement, poisoning (sulfur, oxygenates)
Solution: Pd alloying (Pd–Ag, Pd–Au) for improved durability
Application 5: Palladium Nanoparticles and Research Applications
Why It Matters
Nanotechnology research heavily relies on Pd nanoparticles for catalysis, electrocatalysis, and material science.
Key Notes
Pd source: palladium nitrate solution provides controlled Pd²⁺
Reduction: NaBH₄ (small size), alcohol thermal reduction (controlled size)
Stabilizers: PVP, CTAB, citric acid
Particle size: 2–50 nm, tunable by precursor concentration and reduction conditions
Applications: catalytic studies, surface science, nanoparticle deposition on supports
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Toxicity: Pd²⁺ and nitrates are hazardous; use PPE and fume hoods.
Oxidizing risk: Store away from reducing agents and combustibles.
Waste handling: Recover Pd from waste, neutralize nitrates, comply with regulations.
Conclusion
The five main applications of palladium nitrate solution are:
1.Catalyst precursor for cross-coupling reactions
2.Supported catalysts for hydrogenation
3.Electronic materials and metallization
4.Hydrogen sensors and fuel cells
5.Nanoparticles and research formulations
With precise control of concentration, loading, and reduction, this solution remains a cornerstone material in both industrial chemistry and advanced research.
Ready to Accelerate Your Research?
For technical datasheets, sample requests, or customized catalyst solutions, contact the UIV CHEM technical support team today. Let us help you achieve breakthrough results in organic synthesis and materials innovation!