What is Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride?
Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (CBDA) is an organic dianhydride compound with the molecular formula C₈H₄O₆, consisting of a cyclobutane ring and four carboxyl groups. Due to its symmetric dianhydride structure and unique alicyclic backbone, CBDA plays a significant role in the synthesis of polyimide materials.
Key Parameters of Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
Chemical Name:Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
Abbreviation:CBDA
Molecular Formula:C₈H₄O₆
Molecular Weight:196.11 g/mol
CAS No.:4415-87-6
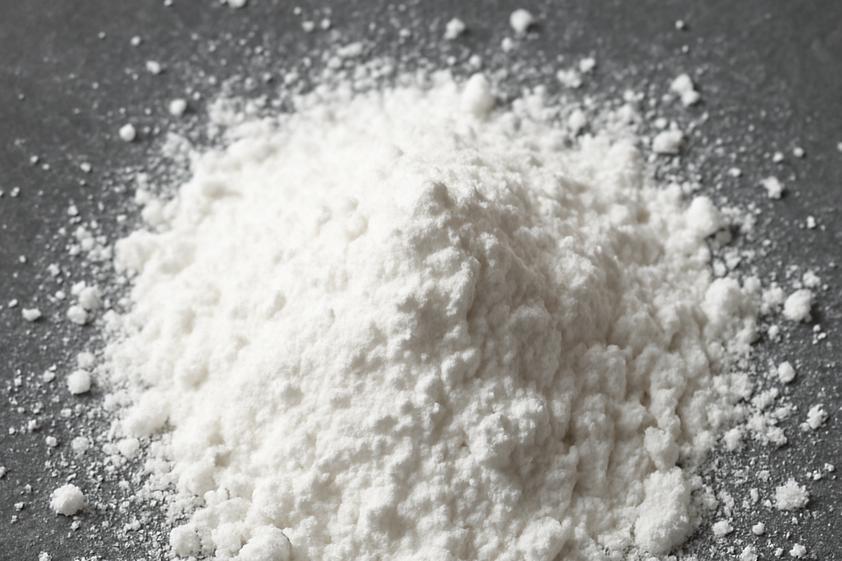
Appearance:White to off-white crystalline powder
Melting Point:290–300 °C (decomposes)
Solubility: Insoluble in water; soluble in polar organic solvents (e.g., NMP, DMF)
These parameters are essential for both research applications and industrial production, providing a reliable reference for material selection.
Functions of Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
Polyimide Monomer
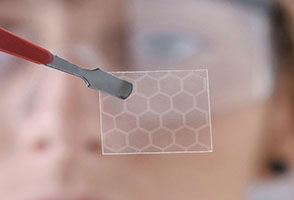
CBDA is a critical dianhydride monomer for producing high-performance polyimides. Compared with traditional aromatic dianhydrides, it enhances transparency and flexibility.
Improved Optical Properties
Since CBDA lacks aromatic rings, it minimizes light absorption, resulting in higher optical transmittance—ideal for optics and display technologies.
Low Dielectric Constant
The alicyclic structure reduces polarity, making CBDA-derived polyimides suitable as low-k materials for high-speed communication and microelectronic insulation.
Enhanced Thermal and Dimensional Stability
The cyclobutane ring imparts rigidity and heat resistance, ensuring stable performance under high-temperature conditions.
Applications of Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
1. Electronics and Semiconductors
-
Used to produce transparent polyimide films, widely applied in flexible displays (OLED, foldable screens).
-
Applied as a low-dielectric polyimide material in 5G/6G communication systems, improving signal transmission efficiency.
2. Aerospace Industry
CBDA-based polyimides exhibit high strength and thermal resistance, making them suitable for lightweight composites in spacecraft, engines, and thermal insulation materials.
3. Optics and Optoelectronics
Transparent polyimides synthesized from CBDA are used in optical waveguides, optical films, and communication components.
4. Insulation and Protective Coatings
CBDA-derived polymer coatings provide excellent insulation and chemical stability, ideal for electronic component protection and packaging.
Future Outlook for Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride
With the rapid development of flexible electronics, optical materials, and high-speed communications, the demand for transparent, low-dielectric polyimides continues to grow. CBDA, thanks to its low-k properties, high transparency, and excellent thermal stability, is expected to become a core monomer for next-generation advanced polymer materials.
Conclusion
Cyclobutane-1,2,3,4-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (CBDA) is a unique alicyclic dianhydride monomer with significant advantages in polyimide synthesis, optoelectronics, telecommunications, and aerospace applications. With the rising demand for transparent, thermally stable, and low-dielectric materials, CBDA is set to play an increasingly critical role in the development of next-generation high-performance polymers.
Ready to Accelerate Your Research?
For technical datasheets, sample requests, or customized catalyst solutions, contact the UIV CHEM technical support team today. Let us help you achieve breakthrough results in organic synthesis and materials innovation!