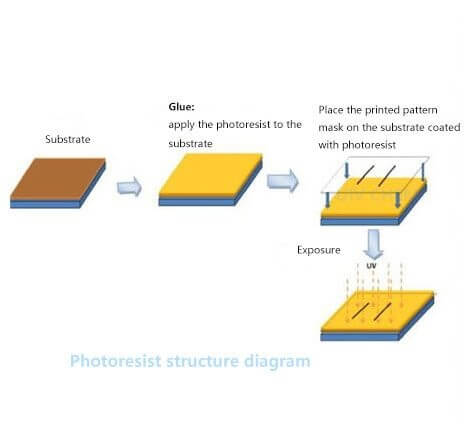
Photoresist is produced not only for general needs, but also for specific needs. It is tuned to different wavelengths of light and exposure sources. In addition, photoresists have specific heat flow properties, are prepared by specific methods, and incorporate specific surfaces. These properties are determined by the type and amount of different chemical components of the photoresist and the mixing process.
Photoresist Components
Photoreceptor
controls and regulates the chemical reaction of the photoresist during the exposure process.
Polymer
When a polymer is exposed to a photoresist, its structure changes from soluble to polymer. Polymers are special light- and energy-sensitive polymers that typically include carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Solvent
The largest component of the photoresist, used to dilute the photoresist and keep the photoresist in a liquid. The solvent used for negative photoresists is aromatic xylene, while the solvent used for positive photoresists is ethyl ethoxyacetate.
Photosensitizer
Added to the photoresist to limit the spectral range of the reacting light or to restrict the reacting light to a specific wavelength.
Additives
Different types of additives and photoresists are mixed together to achieve a specific effect.
Types of photoresists
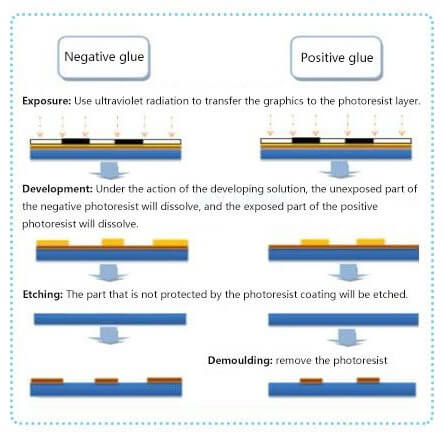
Basically, the classification of photoresists can be divided into two categories: positive and negative.
Positive Photoresists
The basic polymer of positive photoresists is a phenolic polymer. In photoresists, the polymer is relatively insoluble. When the photoresist is exposed to UV light, the chemical structure changes and the photoresist becomes soluble, called photolysis reaction. And the region of photoresist that is not exposed to UV light is insoluble in photoresist developer.
Positive photoresists are generally characterized by high resolution, good step coverage, and good contrast. Positive photoresists are able to maintain their size and pattern because the photoresist developer solvent does not penetrate into areas that are not exposed to UV light. At the same time, there are problems such as poor adhesion, poor etch resistance and high cost.
Negative Photoresists
In the case of negative photoresists, exposure to UV light causes the chemical structure of the photoresist to polymerize, which is the opposite of positive photoresists. In fact, these polymers form a cross-linked substance, i.e., an etch-resistant substance. Therefore, to prevent accidental exposure, negative photoresists are made under yellow light conditions.
The advantages of negative photoresist are good adhesion, good barrier effect, and fast sensitization speed. However, it will deform and expand when developing, which limits its resolution, so generally negative photoresist is only used in the field of large online width.
At last
Both positive and negative photoresists are still used in the semiconductor manufacturing industry today, but many semiconductor suppliers choose positive photoresists because of their ability to provide higher resolution. Negative photoresists offer faster sensitization speeds, a wider process range and significantly lower operating costs. They each have their own usefulness.
UIV Chem is a future-oriented scientific enterprise, and our excellent products have served many leading companies in the fields of OLED display (photoresist is the important material for OLED screen), OLED lamp, environmental protection, new energy, chemistry, medicine, biology, etc., and led a lot of technological innovation in the industry.For more information about photoresists, please contact us.