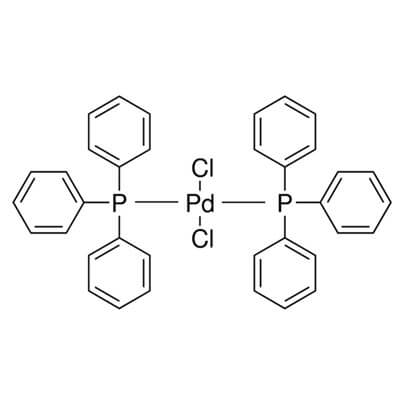
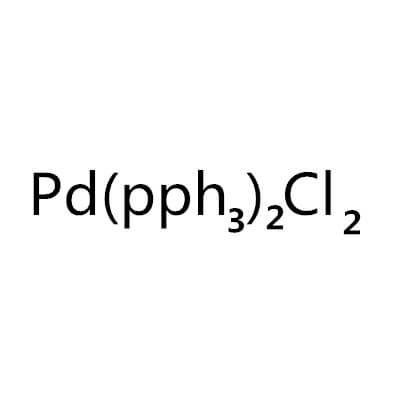Bis(Triphenylphosphine)Palladium(II) Chloride
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride |
| Synonyms |
|
Palladium(II)bis(triphenylphosphine) dichloride;
Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride
[(C6H5)3P]2PdCl2; Palladium(II)bis(triphenylphosphine) dichloride;
|
|
|
||
| Molecular Structure |
|
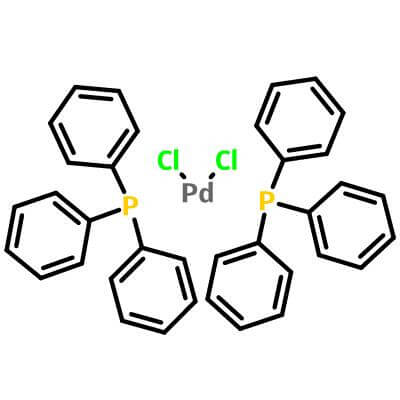 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C36H30Cl2P2Pd |
| Molecular Weight |
|
701.91 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
13965-03-2 |
| EINECS |
|
237-744-2 |
| Properties | ||
|
Melting point |
|
260°C |
| purity |
|
Purity of original palladium powder > 99.99% |
|
Color |
|
Yellow |
|
Shape |
|
Powder |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xn |
| Risk Codes |
|
R22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Description |
|
S26;S37/39 |
Preparation of Bis(Triphenylphosphine)Palladium(II) Chloride:
Add 10g of triphenylphosphorus and 45g of water into a dry single-necked bottle, and stir the electromagnetically to make the system uniform; then add 3g of palladium chloride into the single-necked bottle at one time, stir and react at room temperature for 70min, observe that the material in the bottle gradually changes from black It turns into yellow-earth yellow until the black disappears, that is, the reaction is complete. After the reaction is complete, filter and vacuum dry the filter cake to obtain a yellow solid, which is bis(triphenylphosphonium) palladium dichloride, with a yield of 100%.
Bis(Triphenylphosphine)Palladium(II) Chloride Application:
Bis(triphenylphosphine) palladium chloride can be used as a catalyst for organic synthesis. It is mostly used in suzuki reaction. The carboxylic acid can be decarboxylated under the catalyst of catalytic amount of bis(triphenylphosphine) palladium chloride to form α-ene.
Bis(Triphenylphosphine)Palladium(II) Chloride Uses:
As a catalyst, used in coupling reactions such as Suzuki, Kumada, Negishi, etc. Uses are mainly used in coupling reactions such as Sonogoshira coupling; catalyst for carbonylation of halogenated substances; halogenated alkanes to aldehydes, carboxylic acids, amides, etc.; halogenated alkanes react with acetylene to form carbon Chain growth of alkyne compounds.