Palladium acetate
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Palladium acetate |
| Synonyms |
|
Palladium acetate; Pd(OCOCH3)2 |
|
|
||
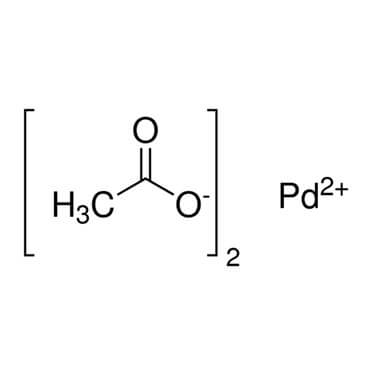
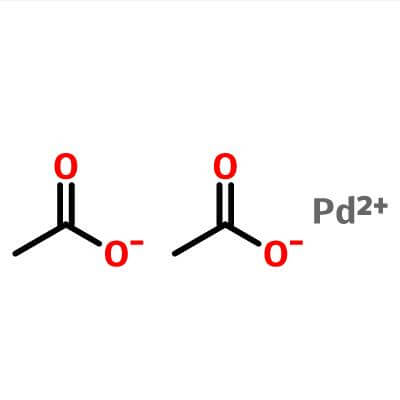
| Molecular Structure |
|
 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
Pd.(C2H3O2)2; Pd(OCOCH3)2 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
224.51 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
3375-31-3 |
| EINECS |
|
222-164-4 |
| Properties | ||
| Pd content |
|
47.4% |
| Specification |
|
Analytical pure |
| Packing |
|
5g,10g,100g,1kg or packed on the clients' requirements |
|
Maximum wavelength (λmax) |
|
400nm(EtOH) |
| Melting point |
|
205 ºC |
| Water solubility |
|
insoluble |
| Appearance |
|
Yellowish brown powder |
|
Solubility |
|
Soluble as monomer in glacial acetic acid or as trimer in benzene. |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xi |
| Risk Codes |
|
R41 |
| Safety Description |
|
S26;S39 |
Palladium acetate application:
Palladium acetate is a widely used palladium compound. In addition to being an important raw material for palladium plating baths and gas-sensitive materials, as well as a raw material for the synthesis of other palladium compounds, it is mainly used as a catalyst that plays a key step in the synthesis of drugs or pharmaceutical intermediates. Mainly used for olefin aromatization reaction (Heckreaction), cross-coupling reaction, Suzuki coupling reaction. At the same time, it can also be applied to the alkene carbonylation reaction and the oxidation reaction of alkene and 2-alcohol to ketone. It is very useful in the industry of cyclohexanone, adipic acid and caprolactam, and is also used in the field of nonlinear optical material synthesis.
Palladium acetate preparation:
Palladium acetate was first synthesized by Heffer [1], and its process is made by boiling sponge palladium in the presence of a small amount of nitric acid and refluxing with glacial acetic acid. After several improvements, nitric acid was changed to perchloric acid, oxygen, NO+O2, NO2, NO+NO2, etc. At the same time, glacial acetic acid was added to hot palladium sulfate aqueous solution to prepare palladium acetate. However, the obvious disadvantages of the process are (1) the reflux reaction time is long, the operation is complicated, and the reaction is not complete, the batch is increased, and the performance is more prominent; (2) if oxygen is used as the oxidant, the reaction must be carried out at 810614kPa, and the equipment and operation are complicated. (3) The source of raw materials such as NO and NO2 is difficult; (4) The above reaction may generate a pink insoluble polymer with no catalytic activity.
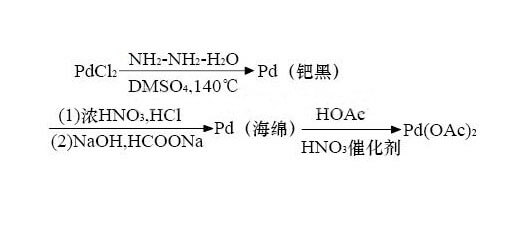
Palladium acetate uses:
Color crystalline powder, soluble in benzene, toluene, insoluble in ether and alcohol, and stored in cold storage away from light.
Catalyst for formation of allyl acetate; catalyst for hydrogenation of selenium to form triple bond; catalyst for olefin Heck arylation reaction; catalyst for cyclocarbonylation reaction; catalyst for Buchwald-Hartwig amination reaction; intramolecular coupling of aryl bromide and alcohol Co-reaction to generate 1,3-oxazepine catalyst; palladium-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization reaction to prepare cyclic urea; a non-halide palladium (II) complex, used as a catalyst for the coupling reaction, and as a precursor For the preparation of heterogeneous catalyzed palladium-containing materials.