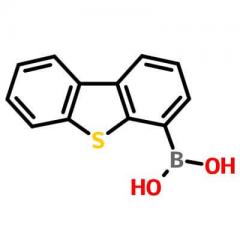
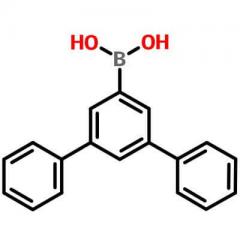
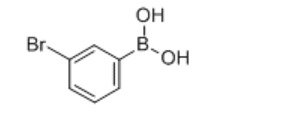
| Identification | ||
| Name | Gallic acid | |
| Synonyms |
3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid Pyrogallol-5-carboxylic acid |
|
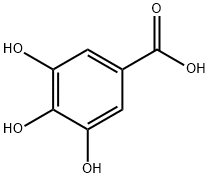
| Molecular Structure |
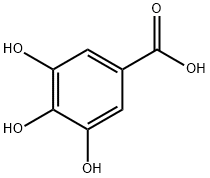
|
|
| Molecular Formula | C7H6O5 | |
| Molecular Weight | 170.12 | |
| CAS Registry Number | 149-91-7 | |
| EINECS | 205-749-9 | |
| Properties | ||
| Density | 1.694 | |
| Melting point | 251 ºC | |
|
Boiling point |
|
259.73°C |
| Water solubility | 12 g/L cold water | |
| refractive index | 1.5690 | |
| pka |
|
4.41 |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols | Xi | |
| Risk Codes | R36/37/38 | |
| Safety Description | S24/25 | |
Gallic acid uses:
1、Gallic acid A cyclooxygease inhibitor substance found in plants.
2、Gallic acid is a potential bleaching agent and anti-oxidant, it is also astringent and potentially anti-microbial and anti-fungal. Scientists are finding that gallic acid may serve as a skin-lightening agent by inhibiting the action of the tyrosinase and peroxidase enzymes. Some studies indicate that it is more effective than hydroquinone when combined with the proper ingredients. It is also incorporated into anti-aging formulations for its ability to prevent mucopolysaccaride deterioration. It is a constituent of witch hazel and oak bark, among many other plants; however, it is generally obtained from nutgalls for commercial purposes.




![(10-[1,1'-Biphenyl]-2-yl-9-anthracenyl)boronic acid,400607-48-9,C26H19BO2](http://resourcewebsite.singoo.cc/14733039928352490/en/image/phone_5bbf0d6e2d1a8.png)