| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Allyl methacrylate |
|
Synonyms |
|
methylacrylic acid-allyl ester; 2-Methyl-2-propenyl 2-propenoate; prop-2-enyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate; Acryester A; prop-2-enyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate; |

|
||
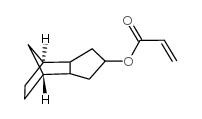
| Molecular Structure |
|
|
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C7H10O2 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
126.15 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
96-05-9 |
| EINECS |
|
202-473-0 |
| Properties | ||
| Density |
|
0.93 |
| Melting point |
|
-65 ºC |
| Boiling point |
|
144 ºC |
| Refractive index |
|
1.435-1.437 |
| Flash point |
|
37 ºC |
| Water solubility |
|
4 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
T;N |
| Risk Codes |
|
R10;R21/22;R23;R50 |
| Safety Description |
|
S36/37;S45;S61 |
| Transport Information |
|
UN 2929 |
It is widely used as a comonomer, grafting monomer and crosslinking agent for tooth repair in the preparation of plexiglass.
Allyl methacrylate is an important crosslinking agent, which can provide the second stage of effective bifunctional crosslinking, with good chemical resistance, impact strength, adhesion, hardness and low water shrinkage. Used in dental materials, industrial paints, organic silicon intermediates, light stabilizers, optical polymers, elastomers and some vinyl and acrylic polymer systems.
Production method of allyl methacrylate:
It can be obtained by the reaction of acrylamide and allyl alcohol under the action of concentrated acid and H2O2, or it can be obtained by transesterification of allyl acetate and methyl methacrylate. It can also be prepared by reacting methacrylic acid with allyl alcohol, using p-toluenesulfonic acid as a catalyst and refluxing in the presence of the polymerization inhibitor hydroquinone. The water produced is continuously removed during the reaction. After the reaction is completed, the excess is recovered by fractional distillation. Allyl alcohol, the product is purified by distillation under reduced pressure.