| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Deuterobenzene |
| Synonyms |
|
Hexadeuteriobenzene; |
|
|
||
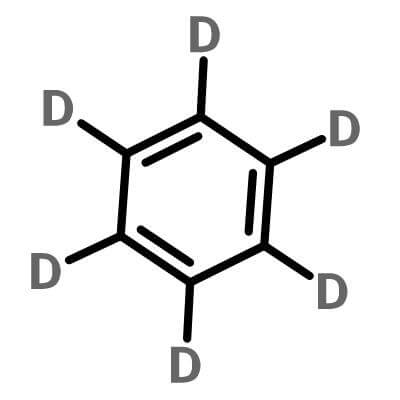
| Molecular Structure |
|
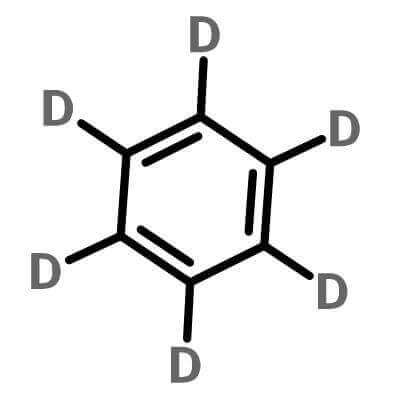 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C6D6 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
84.15 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
1076-43-3 |
|
EINECS |
|
214-061-8 |
| Nature | ||
|
Density |
|
0.9456 |
|
Boiling point |
|
79°C |
|
Melting point |
|
7ºC |
|
Flash point |
|
-11ºC |
|
Purity |
|
≥99.5% |
|
Refractive index |
|
1.4997 |
|
Appearance |
|
Clear colorless liquid |
|
Isotopic Purity (NMR) |
|
≥99.5% |
| Safety Data | ||
|
Hazard Symbols |
|
F;T |
|
Risk Codes |
|
R45;R46;R36/38;R48/23/24/25;R65 |
|
Safety Description |
|
S53;S45 |
|
Transport Information |
|
UN 1114 |
|
HS Code |
|
29022000 |
Introduction of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexadeuteriobenzene:
1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexadeuteriobenzene is a form (called an isotopologue) of benzene (C6H6) in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D") . Deuterated benzene is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
1,2,3,4,5,6-hexadeuteriobenzene uses:
(1)Deuterated benzene is an organic compound, a natural component of crude oil, and one of the most basic petrochemical products. An organic compound is a natural component of crude oil and one of the most basic petrochemical products.
(2)1,2,3,4,5,6-hexadeuteriobenzene is a kind of organic material with special functions, which has important applications in biomedical imaging and genetic testing.
(3)1,2,3,4,5,6-hexadeuteriobenzene is a deuterated derivative of benzene, which is a standard purity solvent used for NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) analysis.