Rhodium(II) Acetate Dimer,15956-28-2,Rh2(OAc)4
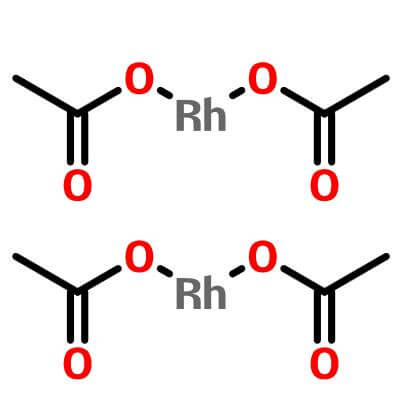
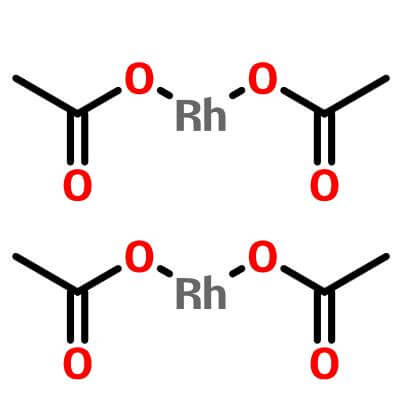
A classic dirhodium(II) catalyst, occupies a central position in metal carbene chemistry due to its unique axial coordination capability and controlled carbene transfer characteristics. Its molecular structure features two rhodium atoms connected by a metalmetal bond, bridged peripherally by four acetate ligands to form a rigid planar structure.
Rhodium(II) Acetate Dimer,15956-28-2,Rh2(OOCCH3)4
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Rhodium(II) acetate dimer |
| Synonyms |
|
Rh2(OAc)4;RHODIUM ACETATE DIMER;DIRHODIUM(II) TETRAACETATE;tetrakis(acetato)dirhodium;tetraac;Rh2(CH3CO2)4;Dimer acid rhodium;RHODIUM(11) ACETATE;dirhodiumtetraacetate;rhodiumdiacetatedimer |
|
|
||
| Molecular Structure |
|
|
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C8H12O8Rh2 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
441.99 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
15956-28-2 |
| EINECS |
|
240-084-8 |
| Properties | ||
| Melting point |
|
205 ºC |
| Purity |
|
> 99.95% |
| Application |
|
catalyst |
| Rh content |
|
46.5% |
| Appearance |
|
Bright green powder |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xi |
| Risk Codes |
|
R36/38 |
| Safety Description |
|
S15;S26;S37/39 |