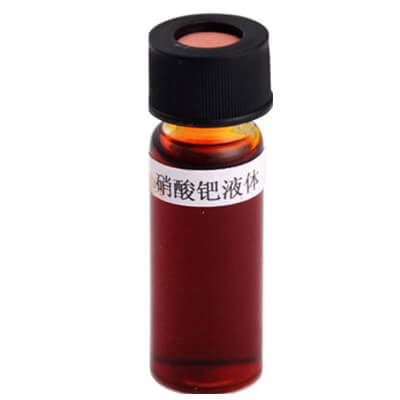
Palladium(II) nitrate solution
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Palladium(II) nitrate solution |
| Synonyms |
|
Palladium(II) nitrate dihydrate
PALLADIUM STANDARD SOLUTION |
|
|
||
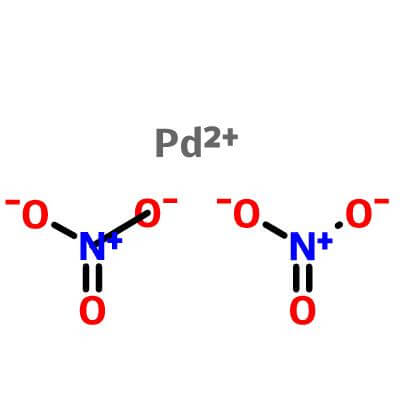
| Molecular Structure |
|
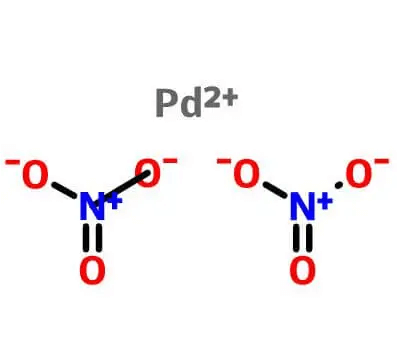 |
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
Pd(NO3)2 |
| Molecular Weight |
|
230.43 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
10102-05-3 |
| EINECS |
|
233-265-8 |
| Properties | ||
| Appearance |
|
Brown liquid |
| content |
|
5%,10% |
|
Density |
|
1.118 g/mL at 25 °C |
|
Solubility |
|
Soluble in dilute nitric acid. |
| Safety Data | ||
| Symbol |
|
GHS05 |
| Signal word |
|
Danger |
| Hazard |
|
statements H314 |
| RIDADR |
|
UN 3264 8 / PGII |
| WGK |
|
Germany 3 |
Palladium(II) nitrate solution preparation:
In theory, palladium can be directly dissolved in nitric acid. Therefore, the commonly used method for preparing palladium nitrate is to add high-purity palladium powder to nitric acid and heat to dissolve to obtain a palladium nitrate solution.
Palladium(II) nitrate solution uses:
Catalyst, raw material for synthesizing a variety of palladium compounds and catalysts. It is used in large quantities to prepare palladium plating bath. Palladium nitrate can be used as a catalyst for the nitration of olefins to ethylene glycol dinitrate; also used as a precursor with a Pd catalyst; Used as analytical reagent and oxidant; also used in the separation of chlorine and iodine; also used in the preparation of active components of automobile exhaust catalysts.