Guanidine thiocyanate _CAS:593-84-0
| Identification | ||
| Name |
|
Guanidine thiocyanate |
| Synonyms |
|
Guanidinium thiocyanate
GTC
GUANIDINE HYDROTHIOCYANATE GUANIDINE ISOTHIOCYANATE
GUANIDINE MONOTHIOCYANATE GUANIDINE RHODANIDE GUANIDINIUM ISOTHIOCYANATE |
|
|
||
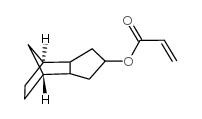
| Molecular Structure |
|
|
|
|
||
| Molecular Formula |
|
C2H6N4S;CH5N3.HSCN |
| Molecular Weight |
|
118.16 |
| CAS Registry Number |
|
593-84-0 |
| EINECS |
|
209-812-1 |
| Properties | ||
| Melting point |
|
118-122 ºC |
|
density |
|
1.103 g/mL at 20 °C |
|
refractive index |
|
1.482 |
| Safety Data | ||
| Hazard Symbols |
|
Xn |
| Risk Codes |
|
R20/21/22;R32;R52/53 |
| Safety Description |
|
S13;S61 |
Guanidine thiocyanate Uses:
Guanidine thiocyanate is a potent protein
denaturant (stronger than guanidine HCl) often used in the isolation of
intact ribonucleic acid to eliminate RNase activity. RNase can recover
activity after boiling, but is irreversibly inactivated in a 4 M
solution of guanidine thiocyanate. Such solutions, to which the reducing
agent b-mercaptoethanol is often added, are used to inactivate RNAse
when isolating RNA from tissues that are rich in RNase, such as liver.
Total nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA may be isolated this way. A protocol
for extracting RNA with guanidine isothiocyanate has been published.
In
the presence of guanidine thiocyanate, proteins dissolve readily,
cellular structures disintegrate and nucleoproteins dissociate from
nucleic acids, as protein secondary structure is lost.